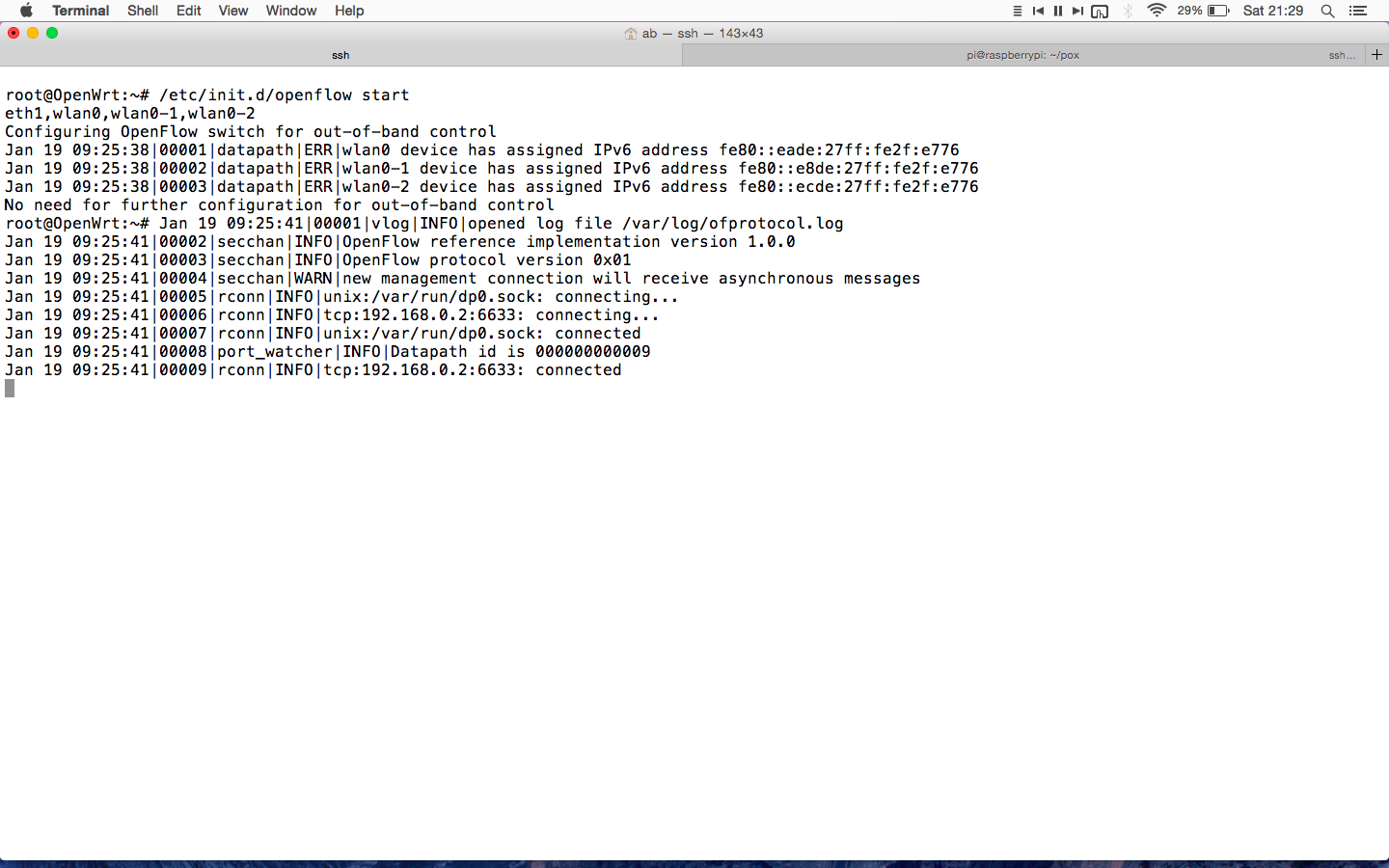
Tutorial No.1
Introduction to Opendaylight
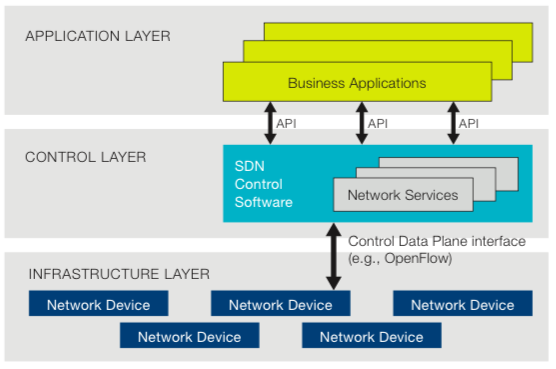
Before getting started with Opendaylight, let me clear one thing that SDn is not only OpenFlow. It is only single standardized protocol by Open Networking Foundation between ofswitch and ofcontroller for SDN. ONF defines SDN as separation of control and data plane which is nothing but how we get SDN is. But if we know what we are getting in SDN we can choose our own path to get SDN.
Now the thing is what SDN gives us is programmability, openness, orchestration, Dynamic Servicing, Simplicity & agility, automation, virtualization of network etc. If this is what SDN is, then I have my own way to get it, said industries.
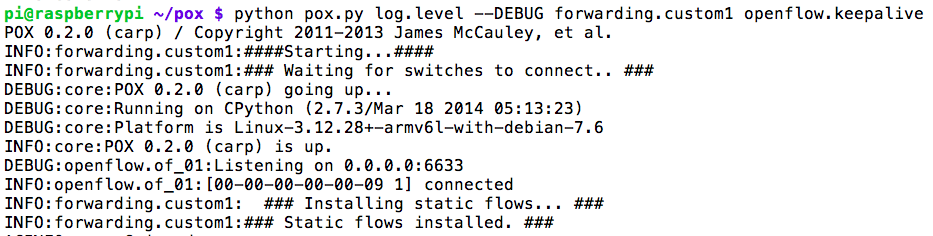
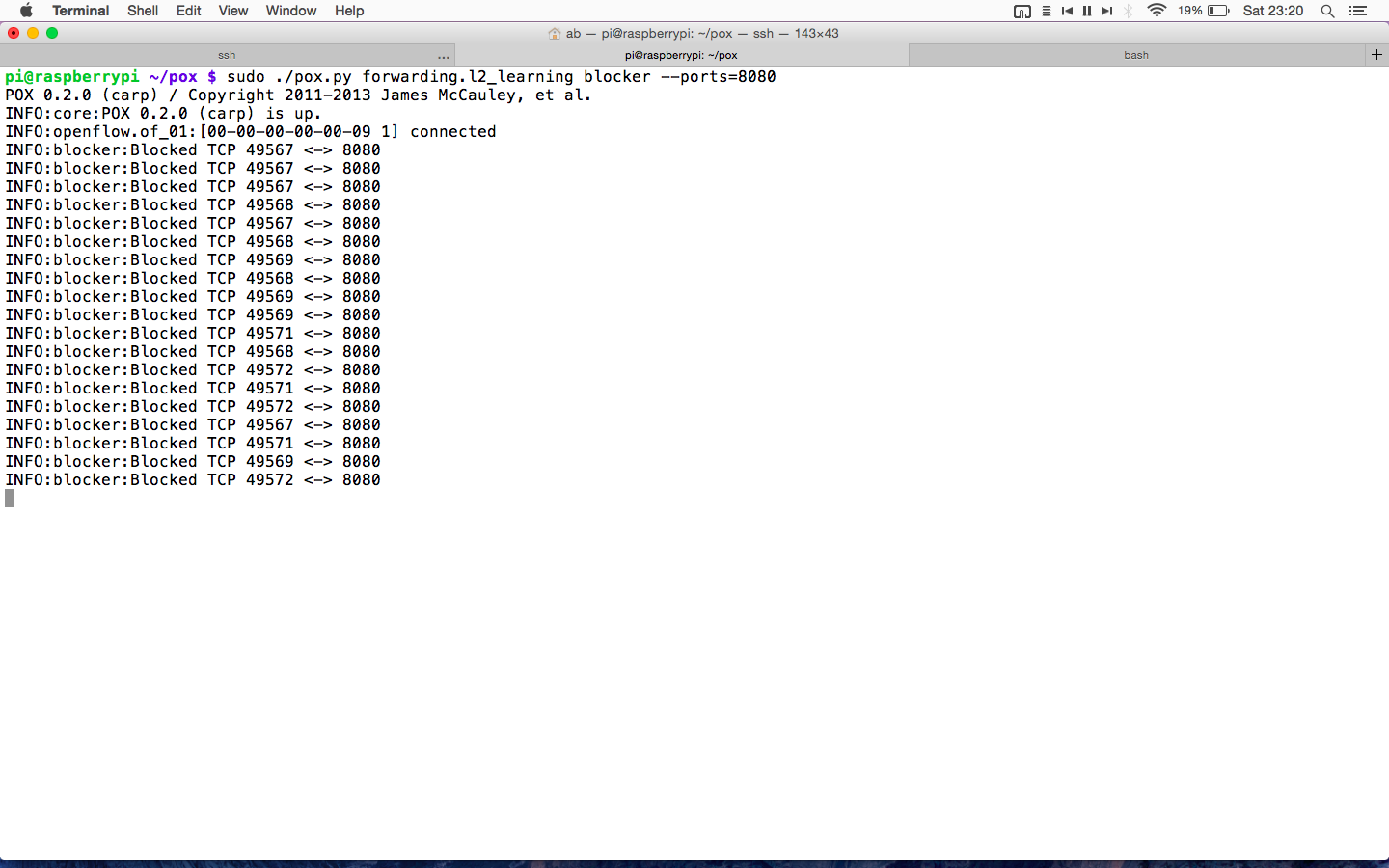
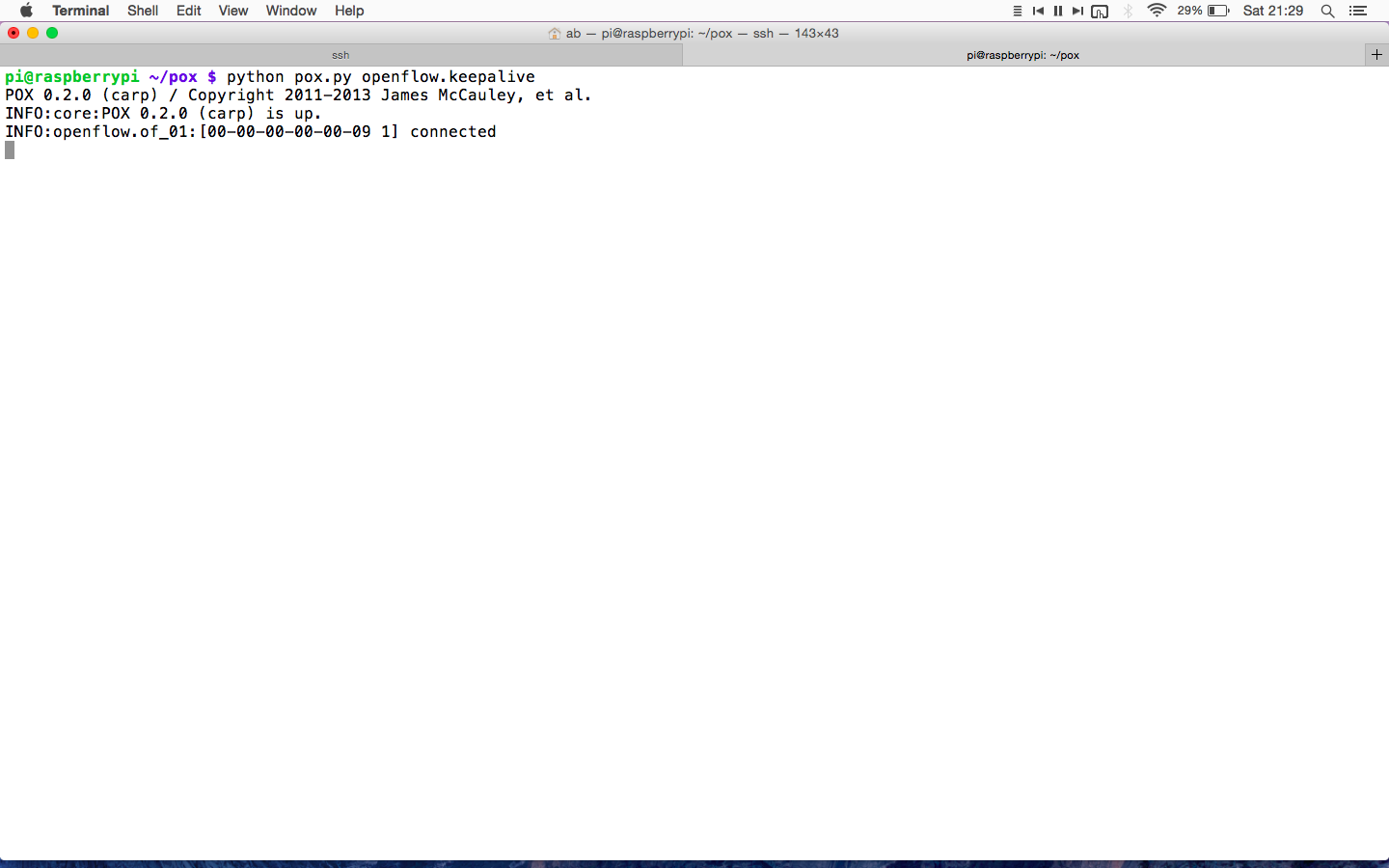
Opendaylight is an open source software project under the Linux Foundation with goal of furthering adoption and innovation of Software Defined Networking through the creation of common industry supported platform. ODL aims to accelerate adoption of Software Defined Networking (SDN) & Network Function Virtualization (NFV).It is officially started on 8th April 2013 and is based on Eclipse Public License v1.0 [EPL].
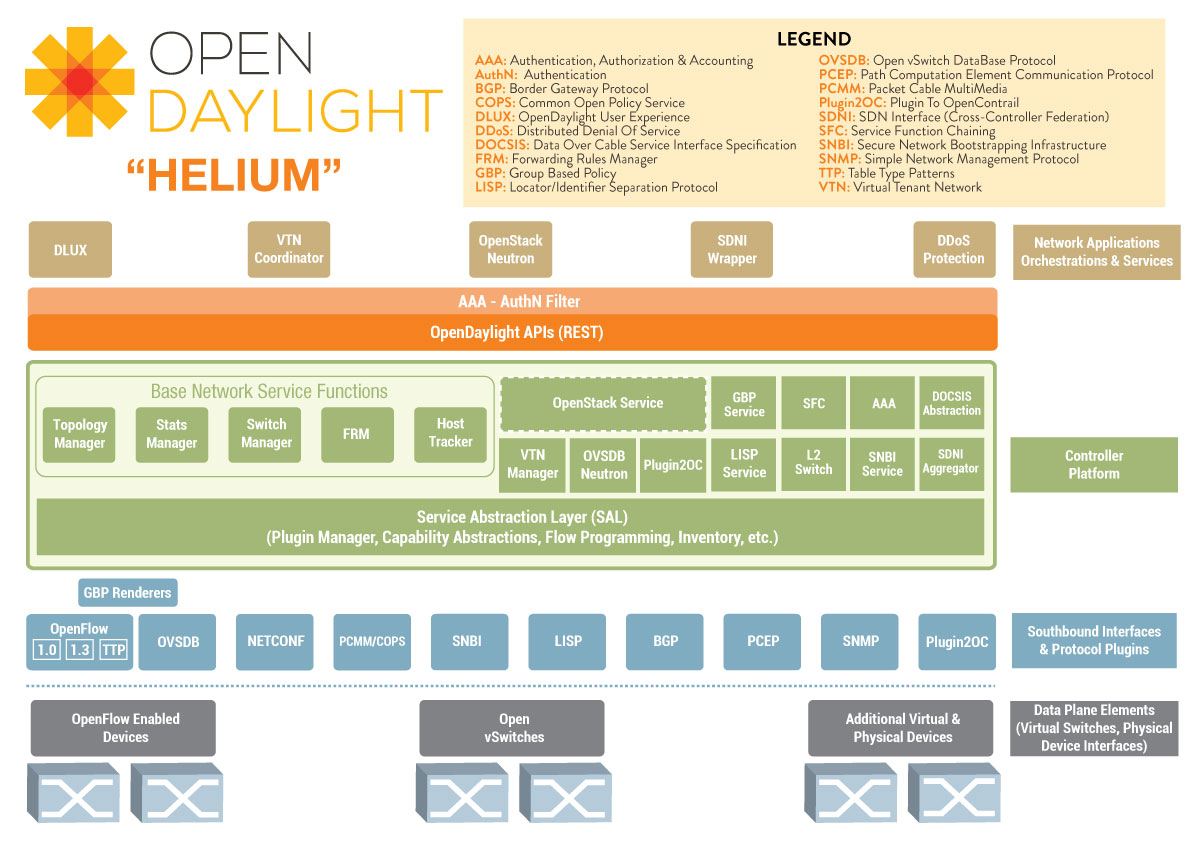
Opendaylight has main three components viz. Network Application & orchestration [management plane], controller platform [control plane], physical-virtual devices [Forwarding plane]. Let’s us try to understand ODL architecture basics. The infrastructure plane may consist physical devices like OpenFlow switches, or virtual devices like openvSwitches. In the management plane there may be GUI/CLI or any cloud mgmt. application like Openstack etc. build on RESTful / JAVA API and OSGI framework. South bound interfaces includes OpenFlow or other protocols like PCE, XMPP, BGP, SMTP, NETCONF etc. This is what the beauty of Opendaylight controller that supports multi-protocols. And these southbound plugins talks to controller platform & network elements via Service Abstrac tion Layer(SAL). And northbound plugins to expose interfaces to those writing applications to the controller. Also pugins for inter controller connection.
Job of SAL is to create a layer against which the application can be developed without assuming the underlying SDN enabling protocol it’s talking about.